Earthing
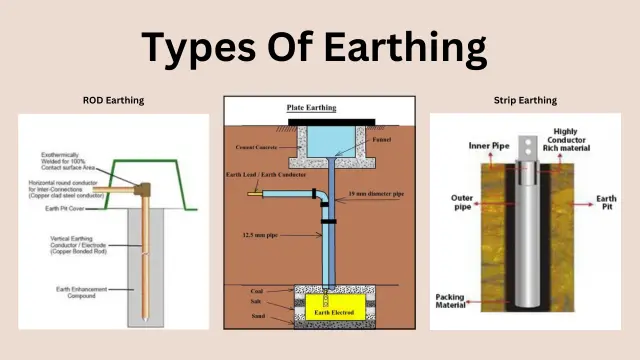
CHEMICAL EARTHING PIPE EARTHING | PLATE EARTHING LIGHTING ARRESTER | EXTERNAL & INTERNAL ELECTRIFICATION POWER & DISTRIBUTION TRANSFORMERS | HT & LT SERVO STABILIZERS | HT & LT PANEL I ON LINE UPS
DIFFERENT TERMS USED IN ELECTRICAL EARTHING
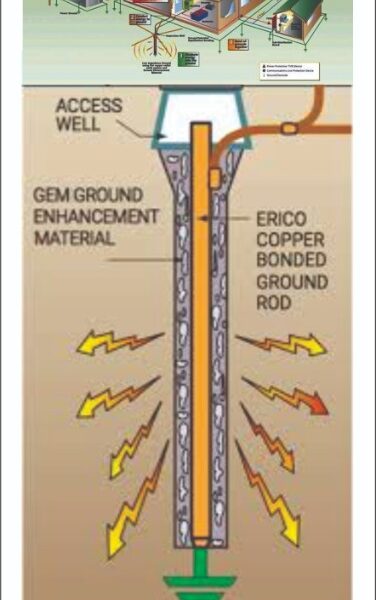
Earth Electrode: When a conductor (or conductive plate) buried in the earth for electrical earthing system. It is known to be Earth Electrode. Earth electrodes are in different shapes like, conductive plate, conductive rod, metal water pipe or any other conductor with low resistance.
Earthing Lead: The conductor wire or conductive strip connected between Earth electrode and Electrical installation system and devices in called Earthing lead.
Earth Resistance: This the total resistance between earth electrode and earth in EPCS. Earth resistance is the algebraic sum of the resistance of earth continuity conductor, earthing lead, earth electrode and earth.
Earth Continuity Conductor: The conductor wire, which is connected among different electrical devices and appliances like, distribution board, different plugs and appliances etc. in other words, the wire between earthing lead and electrical device or appliance is called earth continuity conductor. It may be the shape of metal pipe (fully or partial), or cable metallic sheath or flexible wire.
EARTHING ELECTRODE
Why do earthing and bonding need to be checked?
If you are having an alteration of addition made to your electrical installation, your electrician must check (as well as other things) that the earthing and bonding arrangements you have are up to the required standard.
This is because the safety of any new work you have done (however small) will depend on the earthing and bonding arrangements.
What is earthing?
If there is a fault in your electrical installation you could get an electric shock if you touch a live metal part. This is because the electricity may use your body as a path from the live part to the earth part.
Earthing is used to protect you from an electric shock. It does this by providing a path (a protective conductor) for a fault current to flow to earth. It also causes the protective device (either a circuit-breaker or fuse) to switch off the electric current to the circuit that has the fault.
For example, if a cooker has a fault, the fault current flows to earth through the protective (earthing) conductors. A protective device (fuse or circuit-breaker) in the consumer unit switches off the electrical supply to the cooker. The cooker is now safe from causing an electric shock to anyone who touches it.
What is bonding?
Bonding is used to reduce the risk of electric shocks to anyone who may touch two separate metal parts when there is a fault somewhere in the supply of electrical installation. By connecting bonding conductors between particular parts, it reduces the voltage there might have been.